Universal Law of Gravitation
Universal Law of Gravitation: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as universal law of gravitation, the definition of 'G', units of 'G', and the derivation of Newton’s law of gravitation using Kepler’s third law.
Important Questions on Universal Law of Gravitation
A mass is at the centre of a square, with four masses at the corners as shown:
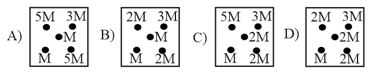
Rank the choice according to the magnitude of the gravitational force of the center mass.
The gravitational force in a region is given by, . The work done by gravitational force to shift a point mass from is
A projectile is launched from the surface of the earth with a very high speed at an angle with vertical. What is its velocity when it is at the farthest distance from the earth surface, given that the maximum height reached by the projectile is equal to the height reached when it is launched perpendicular to earth with a velocity=
Why gravitational force of Earth exerts centripetal force on satellite? Why does the Earth not attract the satellite to collide?
The ratio of S.I. unit to C.G.S. unit of is
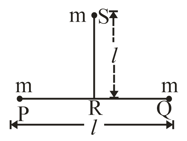
Two particles each of massare placed at points and as shown in the figure. is the mid point of PQ=. The gravitational force on the third particle of mass placed at point on the perpendicular bisector of at distance from R is:-
Consider a ring of mass and radius . Maximum gravitational intensity on the axis of the ring has value
Two particles of mass exert a force on each other. If of mass is transferred from one to other. The force between them is changed by
Find the value of the gravitational constant in CGS system.
Which one of the following statement about gravitational constant and acceleration due to gravity is "TRUE"?
Two small solid spheres each of mass are thrown at the same time with same initial velocity and angle with the horizontal. Sphere is thrown at a height above sphere as shown in the figure. Counting the gravitational force between the two spheres, calculate the change of distance between the two spheres, at the moment sphere hits the ground. You may take the distance between the two spheres as constant in your derivation for the gravitational force because .

When two mass electron are placed at a distance of , calculate force on another proton placed at a distance of from electron?
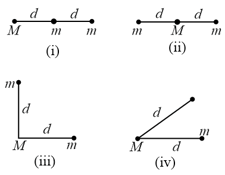
Three particles, two with masses and one with mass , might be arranged in any of the four configurations shown below. Rank the configurations according to the magnitude of the gravitational force on , least to greatest
Two particles of masses and are kept at and respectively. Then the magnitude of net gravitational force acting on a third particle of mass kept at the origin is
What is the dimensional formula for the universal gravitational constant ?
Two identical particles of combined mass , placed in space with certain separation, are released. Interaction between the particles is only of gravitational in nature and there is no external force present. Acceleration of one particle with respect to the other when separation between them is , has a magnitude:
Consider a universe with modified electrostatics where like charges attract and unlike charges repel. Three positively charged point particles with same charge to mass ratio interact with each other through the electrostatic force. Total mass of the system is $M$. The system can move about it's centre of mass with equal distances between all pairs of masses. When the masses are separated by a distance $d$, the angular frequency of the motion about the centre of the mass is
Masses are placed at of an equilateral triangle , being the corners and being midpoint of , if the net-field at the centroid is zero, then
Calculate the gravitational force due to earth on the Mahendra of mass ?
